Maintaining long-term dental health is crucial for preventing oral diseases and preserving a healthy smile throughout life. Oral health not only affects the aesthetics of the teeth but also overall well-being, as dental problems can influence heart health, digestion, and other areas of the body. To achieve lasting dental health, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive approach that combines good oral hygiene habits, regular dental visits, and a healthy lifestyle.
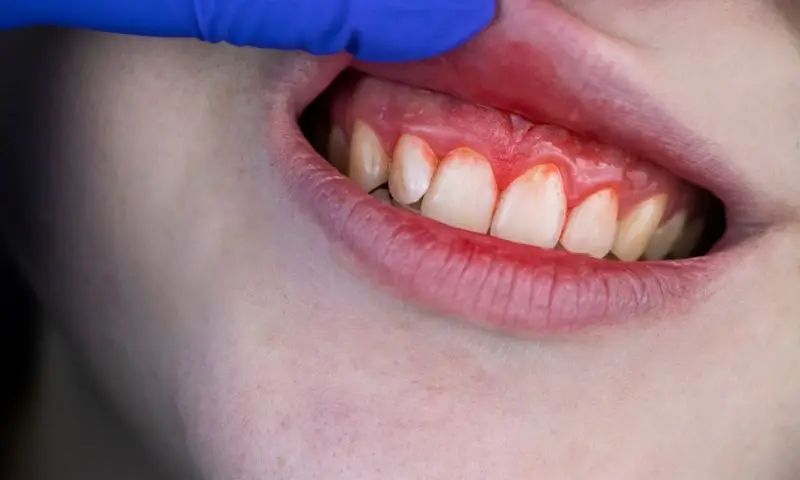
First and foremost, proper oral hygiene is the foundation of long-term dental health. Brushing the teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste is crucial for removing bacterial plaque, the main cause of cavities and periodontal diseases. Additionally, flossing is indispensable for cleaning the areas between the teeth that the brush cannot reach. This helps prevent plaque buildup in these spaces, avoiding issues such as gingivitis or periodontitis.
The use of mouthwashes can also be helpful to complement dental hygiene, especially those containing antibacterial agents that help reduce the amount of bacteria in the mouth and prevent infections. It is also important to avoid harmful habits such as excessive consumption of sugary foods, which promote cavity formation, or tobacco use, which is a risk factor for periodontal diseases and oral cancer.
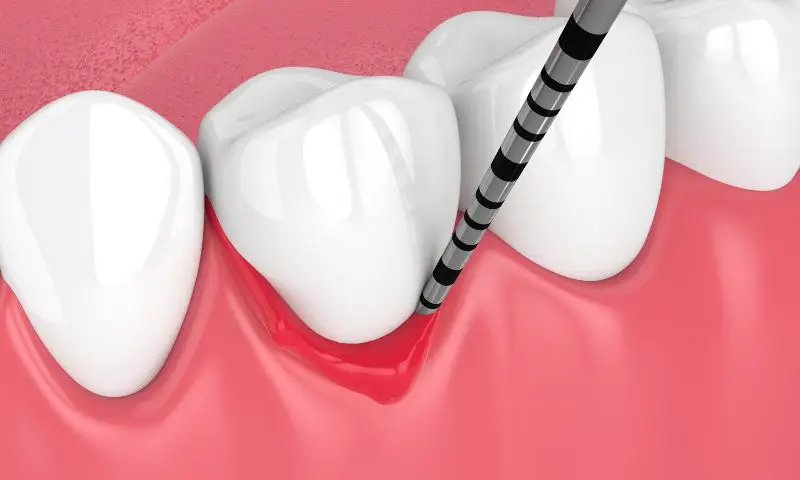
Regular dental visits are essential for maintaining long-term dental health. A routine dental examination allows early detection of problems such as cavities, gum disease, or early signs of oral cancer. The dentist will also perform professional cleanings to remove accumulated tartar and prevent infections. Additionally, the dentist may offer preventive treatments such as fluoride applications or dental sealants to protect the teeth, especially in individuals at higher risk of cavities.
Maintaining dental health also involves a balanced diet, rich in essential nutrients such as calcium and vitamins A and C, which are crucial for the health of the teeth and gums. Avoiding acidic or sugary foods and drinks can reduce the risk of cavities and tooth wear.
Lastly, dental care should not be limited to visible teeth but should encompass all areas of the mouth. The back teeth, gums, and tongue also require constant attention. In this way, proper maintenance of dental health becomes a long-term investment, not only to preserve a beautiful smile but also to safeguard the overall health of the body.