Dental Operation


Dental surgery is a surgical procedure performed by dental professionals to treat various oral conditions, such as infections, gum issues, tooth extractions, or corrections of malformations. These procedures range from simple extractions to more complex treatments, like implants or orthognathic surgery. The main goal is to improve oral health, relieve pain, and restore the functionality of the mouth.
Preoperative care and diagnosis:
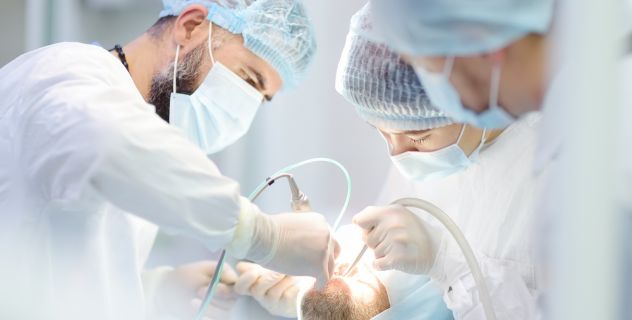
Preoperative care and diagnosis are essential stages in any dental surgical procedure. A proper approach in these phases ensures that the intervention is carried out safely and efficiently, minimizing risks for the patient and optimizing outcomes.
Accurate Diagnosis
The first step in any dental procedure is to make an accurate diagnosis. The dentist must assess the patient’s overall health, medical history, and dental background to identify any conditions that might affect the surgery. This includes reviewing previous illnesses, allergies, and medications the patient is taking. Additionally, tests and radiographs, such as panoramic X-rays or CT scans, are performed to obtain a clear image of the dental and bone structure, facilitating surgical planning. This diagnosis also helps anticipate potential complications and decide the most appropriate anesthesia and surgical approach.
Preoperative Care
Preoperative care aims to prepare the patient both physically and psychologically for the procedure. First, clear instructions are given on how to prepare for surgery, such as fasting for certain hours if general anesthesia will be used. If the patient is taking medications, it is important to follow the dentist’s instructions on whether to temporarily stop or adjust them before the operation. Additionally, in some cases, the dentist may recommend taking antibiotics before surgery to reduce the risk of infections.
It is also crucial that the patient is well-informed about the procedure. A communicative approach helps reduce anxiety and ensures that the patient is fully prepared for what will happen.
In summary, an accurate diagnosis and detailed preoperative care are key to the success of any dental surgery. These steps allow for the anticipation of issues, the selection of the appropriate treatment, and ensure the patient is well-prepared both physically and emotionally for the procedure.
Surgical techniques and anesthesia:
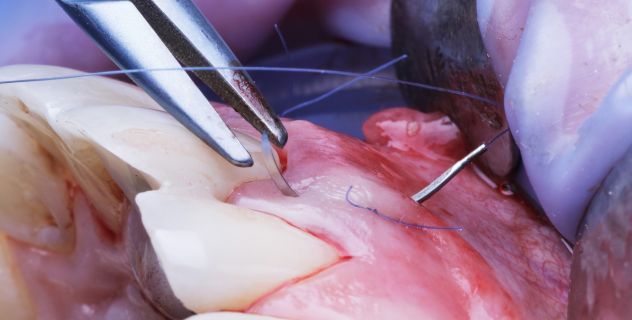
Surgical techniques and anesthesia are fundamental components in any dental procedure that requires surgical intervention, such as complex extractions, implant placement, or periodontal surgeries. Both areas have a direct impact on the patient’s safety and comfort, as well as on the overall success of the operation.
Dental Surgical Techniques
Surgical techniques vary depending on the type of intervention and the complexity of the case. In simpler procedures, such as a routine tooth extraction, the surgery may be minimally invasive, with small incisions and relatively quick recovery. However, in the case of impacted tooth extractions or more complex surgeries, such as dental implant placement, larger incisions and deeper intervention are required.
For example, in dental implant procedures, the surgical technique involves creating a space in the jawbone to insert a titanium screw that will replace the root of the lost tooth. This technique requires precision and, in some cases, a bone graft to ensure a solid base. Periodontal surgery, which treats gum diseases, may also involve procedures such as bone regeneration or gum grafting to restore oral health.
Anesthesia in Dental Procedures
Anesthesia is essential in dental surgical procedures to ensure that the patient does not feel pain during the operation. There are various types of anesthesia used depending on the complexity of the procedure and the patient’s comfort.
Local Anesthesia: In most dental surgeries, such as simple extractions or fillings, local anesthesia is used. This option numbs only the affected area, allowing the patient to remain fully conscious but pain-free. It is administered through an injection into the gums or around the affected nerves.
Conscious Sedation: For more invasive procedures or patients with anxiety, conscious sedation may be used. This combines local anesthesia with a sedative, allowing the patient to be relaxed but still able to respond to the dentist’s instructions.
General Anesthesia: In complex cases or when prolonged interventions are required, general anesthesia is used, which numbs the entire body and puts the patient to sleep throughout the procedure. This type of anesthesia is typically administered in a hospital setting or specialized clinics.
The correct selection of the surgical technique and type of anesthesia is crucial to ensuring a successful dental operation and a quick, complication-free recovery.
Postoperative care and recovery:
Postoperative care and recovery after a dental surgery are essential to ensure proper healing and prevent complications. Depending on the type of procedure, such as a tooth extraction, implant placement, or periodontal surgery, the postoperative approach may vary, but there are common principles that should be followed.
Immediate Postoperative Instructions
In the first few hours after surgery, it is common for the patient to experience swelling, bleeding, and discomfort. To manage these symptoms, it is recommended to apply an ice pack to the affected area, alternating with rest periods. Light bleeding is normal, but if it becomes excessive or persists, the dentist should be contacted. It is also important to follow instructions regarding pain medications, which may include analgesics or antibiotics to prevent infection.
Proper Oral Hygiene
One of the keys to a successful recovery is maintaining good oral hygiene, but without disturbing the operated area. Brushing should be done carefully, avoiding direct contact with the surgical site during the first 24 to 48 hours. Afterward, it is recommended to use a mouthwash with a mild antiseptic to reduce bacterial buildup. In some cases, the dentist may recommend a special rinse to promote healing. It is important to avoid using toothpicks or any objects that could irritate the wound.
Diet and Physical Activity
During the first few days of recovery, it is advisable to follow a soft diet and avoid hard, hot, or spicy foods that may irritate or damage the operated area. Additionally, the patient should avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, as both can delay healing and increase the risk of infection. Regarding physical activity, excessive effort, such as intense exercise, should be avoided, as it can cause bleeding or increase inflammation.
Follow-up and Postoperative Control
It is crucial to attend follow-up appointments with the dentist to ensure that recovery is progressing properly. If signs of infection appear, such as redness, fever, or severe pain, an immediate consultation is necessary. The recovery from a dental operation can take several days or weeks, depending on the scope of the procedure. However, by following postoperative care guidelines, optimal results are achieved, and risks are minimized.
Benefits of Dental Operation
Dental surgery offers significant benefits, such as improved oral health, the elimination of serious dental problems, and the prevention of future complications. It also facilitates orthodontic treatment and improves dental aesthetics.
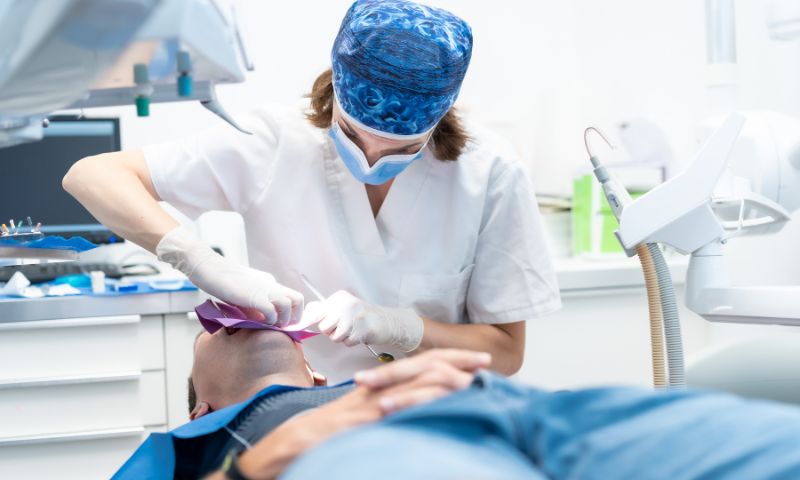
- Relief from severe pain.
- Infection prevention.
- Improving dental aesthetics.
- Facilitates other dental treatments.
- Prevention of future dental problems.
When is dental surgery recommended?
It is recommended when there are serious problems, such as impacted teeth, infections, or untreatable cavities.
Is dental surgery painful?
No, it is performed with local anesthesia to avoid pain during the procedure.
How long does it take to recover from dental surgery?
Initial recovery varies from a few days to two weeks, depending on the surgery.
Can I eat after dental surgery?
Hard and hot foods should be avoided immediately, following the dentist’s instructions.
Is it necessary to take medication after dental surgery?
Yes, to control pain and prevent infection, your dentist may prescribe pain relievers or antibiotics.
We always take care of your smile.
614 415 8236 Call us and schedule your appointment

