Crowns and Bridges

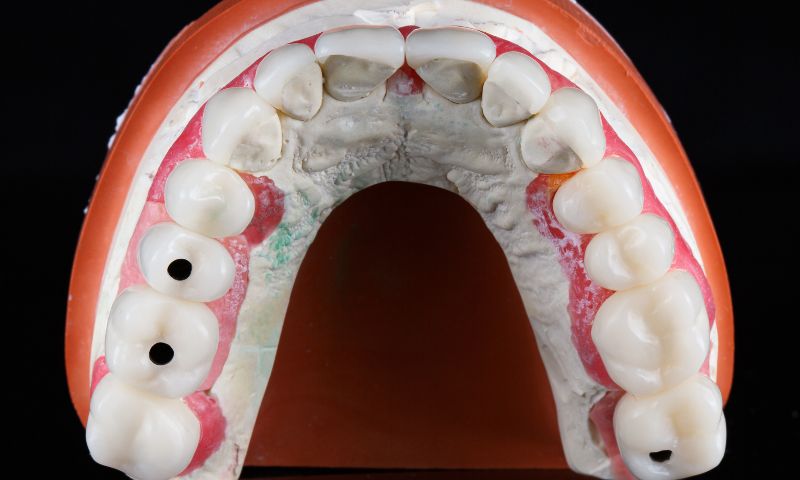
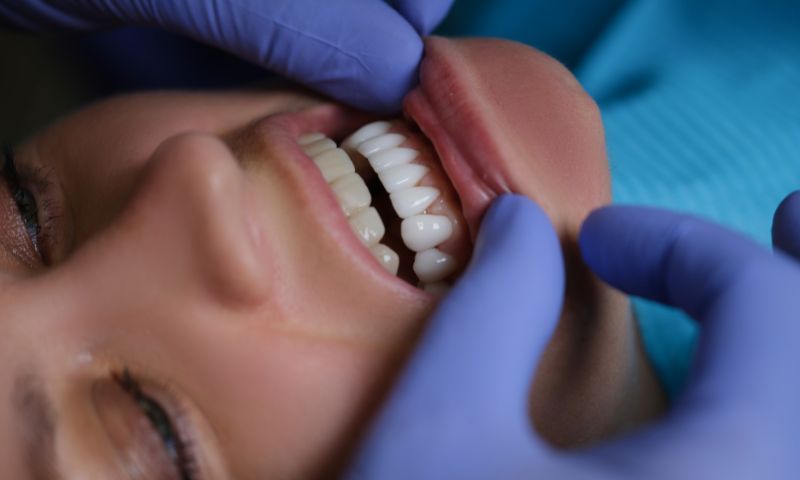
Dental crowns and bridges are effective solutions for restoring damaged or missing teeth. Crowns completely cover a single affected tooth, while bridges replace several missing teeth, using neighboring teeth for support. These procedures, performed by specialized dentists, not only restore oral function but also improve dental aesthetics. With durable materials and advanced technology, they offer natural results and greater smile confidence.
Types of Materials Used:
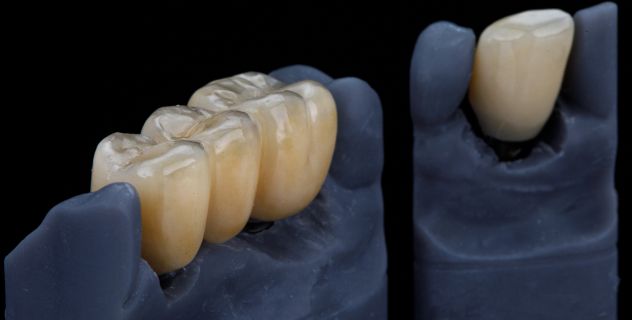
Crowns and dental bridges are commonly used solutions to restore damaged or missing teeth. These treatments are made with different materials, each with its characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. The choice of the right material depends on factors such as durability, aesthetics, cost, and the specific needs of each patient.
Porcelain or Ceramic: Porcelain and ceramic crowns and bridges are highly aesthetic, as they naturally mimic the color and translucency of original teeth. This material is ideal for visible teeth, offering a very realistic appearance. Additionally, porcelain is resistant to stains and discoloration, ensuring a good appearance over time. However, porcelain crowns and bridges may be less durable than other materials, especially in back teeth where chewing pressure is higher.
Metal-Porcelain (Metal-Ceramic): Metal-porcelain crowns and bridges combine the strength of metal with the aesthetics of porcelain. The metal core provides a strong and durable base, while the porcelain layer on the outside enhances the appearance. This material is more durable than pure porcelain and is ideal for back teeth, where greater strength is required. However, the porcelain can wear down over time, and in some cases, the metal may be visible at the edges of the crown or bridge, especially in more receded gums.
Composite Resin: Composite resin crowns and bridges are a more affordable option. This material is relatively easy to mold and, in many cases, fits well with the affected teeth. Composite resin crowns and bridges are less durable than porcelain or metal-porcelain and may be more prone to wear or staining. However, they are useful in situations where a more affordable option is sought, although their lifespan is generally shorter.
Metal: Pure metals, such as gold or platinum, are very durable and resistant to wear. Although not as aesthetic as other materials, metal crowns and bridges are ideal for back teeth, where aesthetics are less important.
Placement Process:
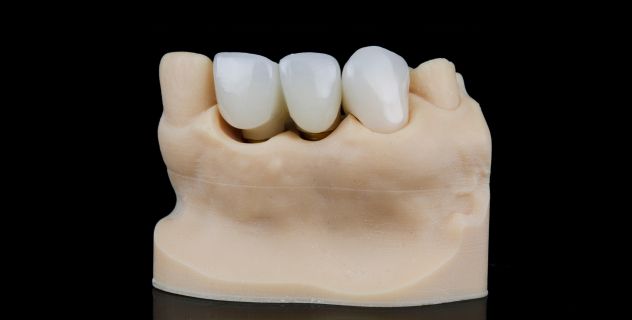
The process of placing crowns and dental bridges is generally carried out in two or three visits to the dentist, depending on the complexity of the case and the type of material used. Below is the common procedure for placing these treatments.
First Visit: Preparation of the Affected Tooth
The process begins with a complete evaluation of the tooth or teeth that need restoration. If the tooth is damaged, the dentist prepares it by reducing its size to ensure that the crown or bridge fits perfectly. In the case of bridges, the dentist also prepares the adjacent teeth that will serve as the pillars for the bridge. This step may require the removal of a significant amount of dental tissue in some cases.
Next, impressions of the affected area are taken, which will be used to make the custom crown or bridge. If the treatment involves a bridge, an impression of the adjacent teeth will also be taken. In some cases, the dentist places a temporary crown to protect the tooth while the permanent piece is being made.
Second Visit: Placement of the Permanent Restoration
Once the crown or bridge has been fabricated in the laboratory (which can take a few days or a week, depending on the material), the patient returns to the dentist for the placement of the permanent piece. The dentist removes the temporary crown, checks the fit and appearance of the new restoration, and makes any necessary adjustments to ensure it fits perfectly and functions properly. After verifying the fit, the crown or bridge is permanently cemented onto the prepared tooth.
Follow-Up Visit: Final Check
In some cases, a follow-up visit may be scheduled to ensure that the restoration is well-fitted and that there are no bite issues or discomfort. The patient will receive instructions on proper care and maintenance to ensure the durability of the crown or bridge.
Care and maintenance:
Proper care and maintenance of dental crowns and bridges are essential to ensure their durability and functionality in the long term. These dental restoration treatments require special attention to avoid complications and maximize their lifespan. Below are the key aspects for caring for crowns and dental bridges.
- Regular Oral Hygiene:
Daily care for crowns and bridges should include a rigorous oral hygiene routine. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a non-abrasive toothpaste is crucial to prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria around the affected area. It’s important to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging the restoration. Additionally, flossing is critical to clean between the teeth and around the crown or bridge. For bridges, special floss for bridges is recommended, as it allows cleaning underneath and removing food particles or plaque that can accumulate.
- Avoid Hard and Sticky Foods:
While crowns and bridges are highly durable, they are not risk-free. Eating hard foods like nuts, hard candies, or ice can damage or even break the restoration. Additionally, sticky foods like chewy candies or gum can adhere to crowns or bridges, increasing the risk of cavities, especially if proper cleaning is not done afterward. It’s important to be cautious with these types of foods, especially during the first few weeks after the restoration is placed.
- Regular Dentist Visits:
Regular visits to the dentist for periodic checkups are essential. Visits every six months allow the dentist to evaluate the condition of the crowns and bridges and check the health of the underlying teeth and gums. Adjustments may also be made if necessary, such as polishing the restoration to maintain its appearance and function.
- Avoid Harmful Habits:
Certain habits, such as nail-biting, using teeth to open packages, or clenching teeth, can put excessive pressure on crowns or bridges, increasing the risk of damage. In cases of bruxism (teeth grinding), the dentist may recommend using a nightguard to protect the restorations.
- Bite Control and Dental Alignment:
Ensuring that the bite is well-aligned is crucial to prevent unnecessary wear on crowns or bridges. If the bite is misaligned, additional pressure may be placed on the restorations. In these cases, the dentist can make adjustments to ensure that the bite is comfortable and functions correctly.
In summary, the care and maintenance of crowns and bridges require a combination of proper oral hygiene, dietary precautions, regular dental visits, and the elimination of habits that may affect the restoration. With these measures, crowns and bridges can last for many years, maintaining both dental health and an aesthetically pleasing smile.
Benefits of Crowns and Bridges:
Dental crowns and bridges restore dental function and aesthetics, improving chewing and a smile. They are long-lasting, customized solutions that increase patient confidence, protect damaged teeth, and prevent future problems.
- Restauran la estética y funcionalidad dental.
- Mejoran la masticación y la digestión.
- Proveen una solución duradera y resistente.
- Protegen dientes debilitados de más daños.
- Aumentan la confianza y autoestima del paciente.
What is a dental crown?
It is a cover that completely covers a damaged tooth to restore its shape, size and function.
How long does a dental crown last?
Depending on the material and care, a crown can last between 10 and 15 years.
What is a dental bridge?
A bridge is a fixed prosthesis that replaces one or more missing teeth, anchoring it to the neighboring teeth..
Do crowns or bridges hurt when they are placed?
They do not usually cause pain during the procedure, although there may be some sensitivity afterward.
Can I eat normally with crowns or bridges?
Yes, you can eat with them, but it is advisable to avoid hard or sticky foods that can damage them.
We always take care of your smile.
614 415 8236 Call us and schedule your appointment

